Depth of Field
The effect descriptions on this page refer to the default effects found within the post-processing stack.
Depth of Field is a common post-processing effect that simulates the focus properties of a cameraA component which creates an image of a particular viewpoint in your scene. The output is either drawn to the screen or captured as a texture. More info
See in Glossary lens. In real life, a camera can only focus sharply on an object at a specific distance; objects nearer or farther from the camera will be somewhat out of focus. The blurring not only gives a visual cue about an object’s distance but also introduces Bokeh which is the term for pleasing visual artifacts that appear around bright areas of the image as they fall out of focus.
An example of Depth of Field effect can be seen in the following images, displaying the results of a focused midground but a defocused background and foreground.

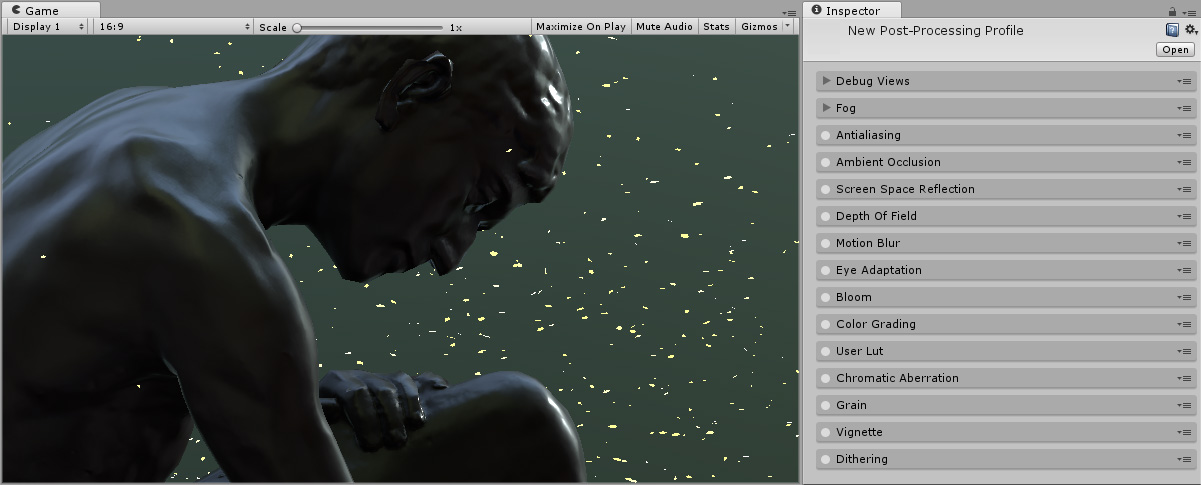
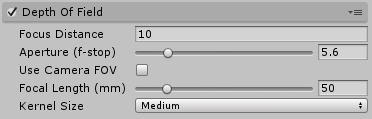
Properties
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Focus Distance | Distance to the point of focus. |
| Aperture | Ratio of the aperture (known as f-stop or f-number). The smaller the value is, the shallower the depth of field is. |
| Focal Length | Distance between the lens and the film. The larger the value is, the shallower the depth of field is. |
| Use Camera FOV | Calculate the focal length automatically from the field-of-view value set on the camera. |
| Kernel Size | Convolution kernel size of the bokeh filter, which determines the maximum radius of bokeh. It also affects the performance (the larger the kernel is, the longer the GPU time is required). |
Optimisation
- Reduce Kernel Size
Requirements
ShaderA small script that contains the mathematical calculations and algorithms for calculating the Color of each pixel rendered, based on the lighting input and the Material configuration. More info
See in Glossary model 3
See the Graphics Hardware Capabilities and Emulation page for further details and a list of compliant hardware.
2017–05–24 Page published with no editorial review
New feature in 5.6