USS supported properties
This topic lists the supported USS properties and their accepted values.
USS data types
USS data types define values and keywords accepted by USS properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
<length> |
Represents a distance value. |
<number> |
Represents either an integer or a number with a fractional component. |
<integer> |
Represents a whole number. |
<color> |
Represents a color. You can define a color with a #hexadecimal code, the rgb() or rgba() function, or a color keyword (for example, blue or transparent). |
<resource> |
Represents an asset in a Resources folder. |
<url> |
Represents an asset specified by a path. It can be expressed as either a relative path or an absolute path. |
USS syntax
UI Toolkit style properties use the same grammar syntax as W3C CSS documents:
- Keyword values appear as is. For example:
auto,baseline. - Basic data types appear between angle brackets (
<and>). For example:<length>,<color>. - Non-terminals that share the same name as a property appear between angle brackets and single straight quotes (
<'and'>). For example,<'width'>.
If a property value has more than one component:
- Side-by-side words mean that all of them must occur in the given order.
- A bar (
|) separates two or more alternatives: exactly one must occur. - A double bar (
||) separates two or more options: one or more must occur, in any order. - A double ampersand (
&&) separates two or more components, all of which must occur, in any order. - Square brackets (
[]) denote grouping.
Every type, keyword, or angle-bracketed group may be followed by modifiers:
- an asterisk (
*) indicates that the preceding type, word, or group occurs zero or more times. - a plus (
+) indicates that the preceding type, word, or group occurs one or more times. - a question mark (
?) indicates that the preceding type, word, or group is optional. - a pair of numbers in curly braces (
{A,B}) indicates that the preceding type, word, or group occurs at leastAand at mostBtimes.
Inherited properties
When no value is specified for an inherited property, the element gets the value from its parent element. For example, use an inherited property to set the font for all elements.
css
:root {
-unity-font: resource("Font/consola.ttf");
}
The following properties are inherited:
- color
- font-size
- -unity-font
- -unity-font-style
- -unity-text-align
- visibility
- whitespace
Box model
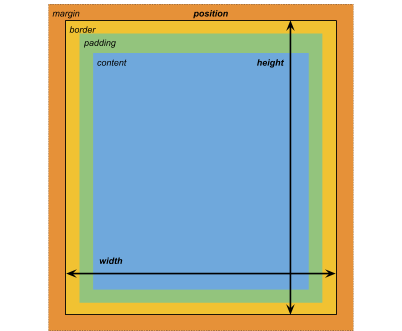
Dimensions
width: <length> | auto
height: <length> | auto
min-width: <length> | auto
min-height: <length> | auto
max-width: <length> | none
max-height: <length> | none
The width and height specifies the size of the element. If width is not specified, the width is based on the width of the element’s contents. If height is not specified, the height is based on the height of the element’s contents.
Margins
margin-left: <length> | auto;
margin-top: <length> | auto
margin-right: <length> | auto
margin-bottom: <length> | auto
Shorthand
margin: [<length> | auto]{1,4}
The margin shorthand options are applied as follows:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 length | Applied to all four margins. |
| 2 lengths | The first is applied to margin-top and margin-bottom. The second is applied to margin-left and margin-right. |
| 3 lengths | The first is applied to margin-top. The second is applied to margin-left and margin-right. The third is applied to margin-bottom. |
| 4 lengths | The lengths are applied in this order : margin-top, margin-right, margin-bottom, margin-left
|
Borders
border-left-width: <length>
border-top-width: <length>
border-right-width: <length>
border-bottom-width: <length>
Shorthand
border-width: <length>{1,4}
The border-width shorthand options are applied as follows:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 length | Applied to all four border widths. |
| 2 lengths | The first is applied to border-top-width and border-bottom-width. The second is applied to border-left-width and border-right-width. |
| 3 lengths | The first is applied to border-top-width. The second is applied to border-left-width and border-right-width. The third is applied to border-bottom-width. |
| 4 lengths | The lengths are applied in this order: border-top-width, border-right-width, border-bottom-width, border-left-width
|
Padding
padding-left: <length>
padding-top: <length>
padding-right: <length>
padding-bottom: <length>
Shorthand
padding: <length>{1,4}
The padding shorthand options are applied as follows:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 length | Applied to all four paddings. |
| 2 lengths | The first is applied to padding-top and padding-bottom. The second is applied to padding-left and padding-right. |
| 3 lengths | The first is applied to padding-top. The second is applied to padding-left and padding-right. The third is applied to padding-bottom. |
| 4 lengths | The lengths are applied in this order: padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom, padding-left
|
Flex layout
This section lists the properties to position visual elements. UI(User Interface) Allows a user to interact with your application. More info
See in Glossary Toolkit includes a layout engine that positions visual elements based on layout and styling properties. The layout engine implements a subset of Flexbox, a HTML/CSS layout system.
By default, all items are vertically placed in their container.
Items
flex-grow: <number>
flex-shrink: <number>
flex-basis: <length> | auto
flex: none | [ <'flex-grow'> <'flex-shrink'>? || <'flex-basis'> ]
align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | stretch
Containers
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse
flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | stretch
align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | stretch
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around
Relative and absolute positioning
Positioning
position: absolute | relative
This property is set to relative by default, which positions the element based on its parent. If this property is set to absolute, the element leaves its parent layout and values are specified based on the parent bounds.
Position
left: <length> | auto
top: <length> | auto
right: <length> | auto
bottom: <length> | auto
The distance from the parent edge or the original position of the element.
Drawing properties
The drawing properties set the background, borders, and appearance of the visual element.
Background
background-color: <color>
background-image: <resource> | <url> | none
-unity-background-scale-mode: stretch-to-fill | scale-and-crop | scale-to-fit
-unity-background-image-tint-color: <color>
Slicing
When assigning a background image, it can be drawn with respect to a simplified 9-slice specification:
-unity-slice-left: <integer>
-unity-slice-top: <integer>
-unity-slice-right: <integer>
-unity-slice-bottom: <integer>
Borders
border-color: <color>
border-top-left-radius: <length>
border-top-right-radius: <length>
border-bottom-left-radius: <length>
border-bottom-right-radius: <length>
Shorthand
border-radius: <length>{1,4}
The border-radius shorthand options are applied as follows:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 length | Applied to all four border-radius properties. |
| 2 lengths | The first is applied to border-top-left-radius and border-bottom-right-radius. The second is applied to border-bottom-left-radius and border-top-right-radius
|
| 3 lengths | The first is applied to border-top-left-radius. The second is applied to border-bottom-left-radius and border-top-right-radius. The third is applied to border-bottom-right-radius. |
| 4 lengths | The lengths are applied in this order: border-top-left-radius, border-top-right-radius, border-bottom-right-radius, border-bottom-left-radius
|
Appearance
overflow: hidden | visible
-unity-overflow-clip-box: padding-box | content-box
opacity: <number>
visibility: visible | hidden
display: flex | none
The display default value is flex. Setting display to none removes the element. Setting the visibility to hidden hides the element, but the element still occupies space in the layout.
The -unity-overflow-clip-box defines the clipping rectangle for the element content. The default is padding-box, the rectangle outside the padding area (the green rectangle in the box model image above); content-box represents the value inside the padding area (the blue rectangle in the box model image above).
Text properties
Text properties set the color, font, font size, and Unity specific properties for font resource, font style, alignment, word wrap, and clipping.
color: <color>
-unity-font: <resource> | <url>
font-size: <number>
-unity-font-style: normal | italic | bold | bold-and-italic
-unity-text-align: upper-left | middle-left | lower-left | upper-center | middle-center | lower-center | upper-right | middle-right | lower-right
white-space: normal | nowrap
Cursor property
Use the cursor default texture type to import a custom texture for the cursor.
cursor: [ [ <resource> | <url> ] [ <integer> <integer>]? , ] [ arrow | text | resize-vertical | resize-horizontal | link | slide-arrow | resize-up-right | resize-up-left | move-arrow | rotate-arrow | scale-arrow | arrow-plus | arrow-minus | pan | orbit | zoom | fps | split-resize-up-down | split-resize-left-right ]
- 2019–05–23 Page amended