Linux Player settings
Use the Linux Unity Player settings (menu: Edit > Project Settings > Player) to determine how Unity builds and displays your Linux application. For a description of the general Player settings, refer to Player SettingsSettings that let you set various player-specific options for the final game built by Unity. More info
See in Glossary.
You can find documentation for the properties in the following sections:
Icon
Enable the Override for Windows, Mac, Linux setting to assign a custom icon for your desktop game. You can upload different sizes of the icon to fit each of the squares provided.
Resolution and Presentation
Use the Resolution and Presentation section to customize aspects of the screen’s appearance in Resolution and Standalone Player Options.
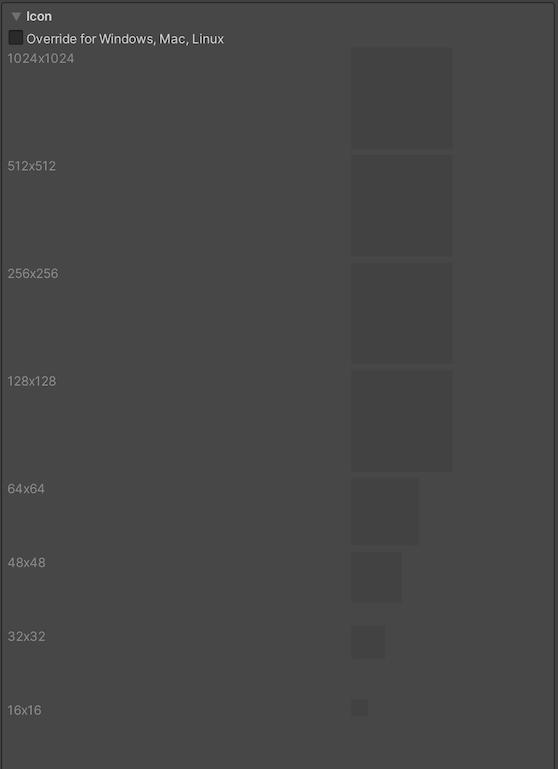
Resolution section
Use this section to customize the screen mode and default size.
| Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Run In background | Enable this option to allow the application to run in the background when it loses focus. When disabled, the application pauses when it loses focus. | |
| Fullscreen Mode | Choose the full-screen mode. This defines the default window mode at startup. | |
| Fullscreen Window | Set your app window to the full-screen native display resolution, covering the whole screen. This mode is also known as borderless full-screen. Unity renders the app content at the resolution set by a script, or the native display resolution if none is set and scales it to fill the window. When scaling, Unity adds black bars to the rendered output to match the display aspect ratioThe relationship of an image’s proportional dimensions, such as its width and height. See in Glossary to prevent content stretching. This process is called letterboxing. The OS overlay UI(User Interface) Allows a user to interact with your application. Unity currently supports three UI systems. More info See in Glossary displays on top of the full-screen window (such as IME input windows). All platforms support this mode. |
|
| Exclusive Fullscreen (Windows only) | Set your app to maintain sole full-screen use of a display. Unlike Fullscreen Window, this mode changes the OS resolution of the display to match the app’s chosen resolution. This option is only supported on Windows. | |
| Maximized Window (Windows and Mac only) | Set the app window to the operating system’s definition of maximized. On Windows, it is a full-screen window with a title bar. On macOS, it is a full-screen window with a hidden menu bar and dock. Fullscreen Window is the default setting for other platforms. | |
| Windowed | Set your app to a standard, non-full-screen movable window, the size of which is dependent on the app resolution. In this mode, the window is resizable by default. Use the Resizable Window setting to disable this. All desktop platforms support this full-screen mode. | |
| Default Is Native Resolution | Enable this option to make the game use the default resolution used on the target machine. Note: This property isn’t visible if you set Fullscreen Mode to Windowed. |
|
| Default Screen Width | Set the default width of the game screen in pixels. Note: This property is visible only if you set Fullscreen Mode to Windowed. |
|
| Default Screen Height | Set the default height of the game screen in pixels. Note: This property is visible only if you set Fullscreen Mode to Windowed. |
|
| Mac Retina Support | Enable this option to enable support for high DPI (Retina) screens on a Mac. Unity enables this by default. This enhances Projects on a Retina display, but it’s somewhat resource-intensive when active. | |
Standalone Player Options
Use this section to specify the settings to customize the screen. For example, you can set options for users to resize the screen and specify the number of instances that can run concurrently.
| Property | Function |
|---|---|
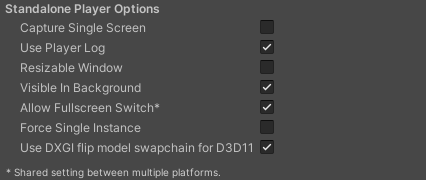
| Capture Single Screen | Enable this option to ensure desktop games in Fullscreen Mode don’t darken the secondary monitor in multi-monitor setups. This isn’t supported on macOS X. |
| Use Player Log | Enable this option to write a log file with debugging information. Defaults to enabled. Warning: If you plan to submit your application to the Mac App Store, leave this option disabled. For more information, refer to publishing to the Mac App Store. |
| Resizable Window | Enable this option to allow resizing of the Player window. Note: If you disable this option, your application can’t use the Windowed Fullscreen Mode. |
| Visible in Background | Enable this option to display the application in the background if the Windowed Fullscreen Mode option is used (in Windows). |
| Allow Fullscreen Switch | Enable this option to allow default OS full-screen key presses to toggle between full-screen and windowed modes. |
| Force Single Instance | Enable this option to restrict desktop players to a single concurrent running instance. |
| Use DXGI flip model swap chain for D3D11 | Use the flip model to ensure best performance for presenting your application. Every time a frame needs to be displayed, Unity makes a copy of the swap chain surface and blitsA shorthand term for “bit block transfer”. A blit operation is the process of transferring blocks of data from one place in memory to another. See in Glossary it to the screen buffer. This setting affects the D3D11 graphics API. Disable this option to fall back to the Windows 7-style BitBlt model. When run in Windowed (borderless) full-screen mode, Unity displays the application swap chain directly on the screen, which reduces input latency by one frame and eliminates desktop composition done by the Desktop Window Manager in the same way that exclusive full-screen does. This optimization is known as “Independent Flip.” For more information, refer to PlayerSettings.useFlipModelSwapchain. |
Splash Image
Use the Virtual Reality Splash Image setting to select a custom splash image for Virtual RealityVirtual Reality (VR) immerses users in an artificial 3D world of realistic images and sounds, using a headset and motion tracking. More info
See in Glossary displays. For common Splash Screen settings, visit the Splash Screen page.
Other Settings
This section allows you to customize a range of options organized into the following groups:
- Rendering
- Vulkan Settings
- Mac App Store Options
- Configuration
- Shader Variant Loading
- Shader Variant Loading Settings
- Script Compilation
- Optimization
- Stack Trace
- Legacy
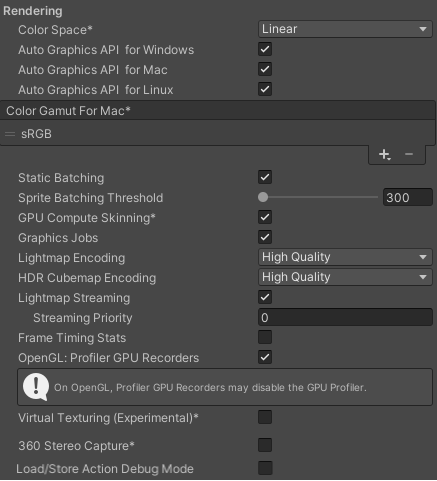
Rendering
Use these settings to customize how Unity renders your game for desktop (Windows, Mac, Linux) platforms.
| Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Color Space | Choose which color space to use for rendering. For more information, refer to Linear rendering overview. | |
| Gamma | Gamma color space is typically used for calculating lighting on older hardware restricted to 8 bits per channel for the framebuffer format. Even though monitors today are digital, they might still take a gamma-encoded signal as input. | |
| Linear | Linear color space rendering gives more precise results. When you select to work in linear color space, the Editor defaults to using sRGB sampling. If your Textures are in linear color space, you need to work in linear color space and deactivate sRGB sampling for each Texture. | |
| Auto Graphics API for Windows | Enable this option to use the best Graphics API for the Windows machine the application runs on. Disable it to add and remove supported Graphics APIs. | |
| Auto Graphics API for Mac | Enable this option to use the best Graphics API for the macOS machine the application runs on. Disable it to add and remove supported Graphics APIs. | |
| Auto Graphics API for Linux | Enable this option to use the best Graphics API for the Linux machine the application runs on. Disable it to add and remove supported Graphics APIs. | |
| color-gamut | This setting doesn’t apply to Linux. | |
| Static Batching | Enable this option to use static batchingA technique Unity uses to draw GameObjects on the screen that combines static (non-moving) GameObjects into big Meshes, and renders them in a faster way. More info See in Glossary. |
|
| GPU Skinning | Enable the use of shaders to calculate mesh skinning and blend shapes on the GPU. | |
| Graphics Jobs | Offload graphics tasks (render loops) to worker threads running on other CPU cores. This option reduces the time spent in Camera.Render on the main thread, which can be a bottleneck. |
|
| Lightmap Encoding | Defines the encoding scheme and compression format of the lightmaps. You can choose from Low Quality, Normal Quality, or High Quality |
|
| HDR Cubemap Encoding | Defines the encoding scheme and compression format of the HDR Cubemaps. You can choose from Low Quality, Normal Quality, or High Quality. For more information, refer to Lightmaps: Technical information. |
|
| Lightmap Streaming | Enable this option to use Mipmap Streaming for lightmaps. Unity applies this setting to all lightmaps when it generates them. Note: To use this setting, you must enable the Texture Streaming Quality setting. |
|
| Streaming Priority | Set the priority for all lightmaps in the Mipmap Streaming system. Unity applies this setting to all lightmaps when it generates them. Positive numbers give higher priority. Valid values range from -128 to 127. |
|
| Frame Timing Stats | Enable this option to gather CPU/GPU frame timing statistics. | |
| Allow HDR Display Output | Activate HDR mode output when the application runs. This only works on displays that support this feature. If the display doesn’t support HDR mode, the game runs in standard mode. | |
| Allow HDR Display Output | Enable HDR mode output when the application runs. This only works on displays that support this feature. If the display doesn’t support HDR mode, the game runs in standard mode. | |
| Use HDR Display Output | Checks if the main display supports HDR, and if it does, swaps to HDR output when the application launches. Note: This option is available only when Allow HDR Display Output is active. |
|
| Virtual Texturing (Experimental) | Enable this option to reduce GPU memory usage and texture loading times if your Scene has many high resolution textures. For more information, refer to Virtual Texturing. Note: The Unity Editor requires a restart for this setting to take effect. |
|
| 360 Stereo Capture | Indicates whether Unity can capture stereoscopic 360 images and videos. For more information, refer to Stereo 360 Image and Video Capture. | |
| Load/Store Action Debug Mode | Highlights undefined pixels that might cause rendering problems on mobile platforms. This affects the Unity Editor Game view, and your built application if you select Development Build in Build Settings. Refer to LoadStoreActionDebugModeSettings for more information. | |
Vulkan Settings
| Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| SRGB Write Mode | Enable this option to let the Graphics.SetSRGBWrite() renderer toggle the sRGB write mode during runtime. Use this to deactivate Linear-to-sRGB write color conversion. | |
| Number of swapchain buffers | Set this option to 2 for double-buffering, or 3 for triple-buffering to use with the Vulkan renderer. This setting might help with latency on some platforms, but usually you shouldn’t change this from the default value of 3. Double-buffering might have a negative impact on performance. | |
| Acquire swapchain image late as possible | Enable this to get the backbuffer after the frame renders to an offscreen staging image. Enabling this setting adds an extra blit when presenting the backbuffer. This setting, in combination with double-buffering, can improve performance. However, it also can cause performance issues as the additional blit uses extra bandwidth. | |
| Recycle command buffers | Enable this option to recycle CommandBuffers after Unity executes them. | |
Mac App Store Options
The properties in this section are only relevant to macOS. For more information, refer to macOS Player Settings.
Configuration
| Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Scripting Backend | Choose the scripting backend you want to use. The scripting backend determines how Unity compiles and executes C# code in your Project. | |
| Mono | Compiles C# code into .NET Common Intermediate Language (CIL) and executes that CIL using a Common Language Runtime. For more information, refer to MonoA scripting backend used in Unity. More info See in Glossary. |
|
| IL2CPP | Compiles C# code into CIL, converts the CIL to C++ and then compiles that C++ into native machine code, which executes directly at runtime. For more information, refer to IL2CPPA Unity-developed scripting back-end which you can use as an alternative to Mono when building projects for some platforms. More info See in Glossary. |
|
| API Compatibility Level | Choose which .NET APIs you can use in your project. This setting can affect compatibility with third-party libraries. However, it has no effect on Editor-specific code (code in an Editor directory, or within an Editor-specific Assembly Definition). Tip: If you are having problems with a third-party assembly, you can try the suggestion in the API Compatibility Level section below. |
|
| .Net Framework | Compatible with the .NET Framework 4 (which includes everything in the .NET Standard 2.0 profile plus additional APIs). Choose this option when using libraries that access APIs not included in .NET Standard 2.0. Produces larger builds and any additional APIs available aren’t necessarily supported on all platforms. For more information, refer to Referencing additional class library assemblies. | |
| .Net Standard 2.1 | Produces smaller builds and has full cross-platform support. | |
| IL2CPP Code Generation | This setting doesn’t apply for Linux. | |
| C++ Compiler Configuraion | This setting doesn’t apply for Linux. | |
| Use incremental GC | Uses the incremental garbage collector, which spreads garbage collection over several frames to reduce garbage collection-related spikes in frame duration. For more information, refer to Automatic Memory Management. | |
| Allow downloads over HTTP | Indicates whether to allow downloading content over HTTP. The default option is Not allowed due to the recommended protocol being HTTPS, which is more secure. | |
| Not Allowed | Never allow downloads over HTTP. | |
| Allowed in Development Builds | Only allow downloads over HTTP in development builds. | |
| Always Allowed | Allow downloads over HTTP in development and release builds. | |
| Active Input Handling | Choose how to handle input from users. | |
| Input Manager (Old) | Uses the traditional Input settings. | |
| Input System Package (New) | Uses the Input system. This option requires you to install the InputSystem package. | |
| Both | Use both systems. | |
API Compatibility Level
You can choose your mono API compatibility level for all targets. Sometimes a third-party .NET library uses functionality that’s outside of your .NET compatibility level. To understand what’s going on in such cases, and how to best fix it, try following these suggestions:
- Install ILSpy for Windows.
- Drag the .NET assemblies for the API compatilibity level you are having issues with into ILSpy. You can find these under
Frameworks/Mono/lib/mono/YOURSUBSET/. - Drag in your 3rd-party assembly.
- Right-click your 3rd-party assembly and select Analyze.
- In the analysis report, inspect the Depends on section. The report highlights anything that the 3rd-party assembly depends on, but that’s not available in the .NET compatibility level of your choice in red.
Mac Configuration
This section is only relevant to macOS. For more information, refer to macOS Player Settings.
Shader Settings
| Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| ShaderA program that runs on the GPU. More info See in Glossary Precision Model |
Select the default precision of samplers and the definition of half used in shaders. Select Unified to set the default sampler precision to full precision, and to enable 16-bit floating point operations in shaders on macOS. For more information, refer to ShaderPrecisionModel. |
|
| Strict shader variant matching | Use the error shader if a shader variant is missing and display an error in the console. | |
| Keep Loaded Shaders Alive | Keep all loaded shaders alive and prevent unloading. | |
Shader Variant Loading Settings
Use these settings to control how much memory shaders use at runtime.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Default chunk size (MB) | Sets the maximum size of compressed shader variant data chunks Unity stores in your built application for all platforms. The default is 16. For more information, refer to Shader loading. |
| Default chunk count | Sets the default limit on how many decompressed chunks Unity keeps in memory on all platforms. The default is 0, which means there’s no limit. |
| Override | Enables overriding Default chunk size and Default chunk count for this build target. |
| Chunk size (MB) | Overrides the value of Default chunk size (MB) on this build target. |
| Chunk count | Overrides the value of Default chunk count on this build target. |
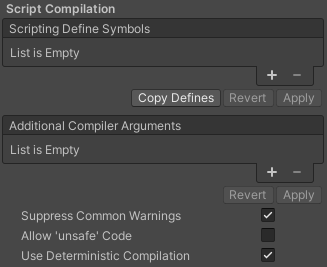
Script Compilation
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Scripting Define Symbols | Sets custom compilation flags. For more details, refer to Platform dependent compilation. |
| Additional Compiler Arguments | Adds entries to this list to pass additional arguments to the Roslyn compiler. Use one new entry for each additional argument. To create a new entry, click Add (+). To remove an entry, click Remove (-). When you have added all desired arguments, click Apply to include your additional arguments in future compilations. Click Revert to reset this list to the most recent applied state. |
| Suppress Common Warnings | Indicates whether to display the C# warnings CS0169 and CS0649. |
| Allow ‘unsafe’ Code | Enables support for compiling ‘unsafe’ C# code in a pre-defined assembly (for example, Assembly-CSharp.dll). For Assembly Definition Files ( .asmdef), click on one of your .asmdef files and enable the option in the Inspector window that appears. |
| Use Deterministic Compilation | Indicates whether to prevent compilation with the -deterministic C# flag. With this setting enabled, compiled assemblies are byte-for-byte the same each time they’re compiled. For more information, refer to C# Compiler Options that control code generation. |
Optimization
| Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Prebake Collision Meshes | Adds collision data to Meshes at build time. | |
| Preloaded Assets | Sets an array of Assets for the player to load on startup. To add new Assets, increase the value of the Size property and then set a reference to the Asset to load in the new Element box that appears. |
|
| Managed Stripping Level | Chooses how aggressively Unity strips unused managed (C#) code. When Unity builds your app, the Unity Linker process can strip unused code from the managed DLLs your Project uses. Stripping code can make the resulting executable smaller, but can sometimes remove code that’s in use. For more information about these options and bytecode stripping with IL2CPP, refer to ManagedStrippingLevel. |
|
| Minimal | Use this to strip class libraries, UnityEngine, Windows Runtime assemblies, and copy all other assemblies. | |
| Low | Remove unreachable managed code to reduce build size and Mono/IL2CPP build times. | |
| Medium | Run UnityLinker to reduce code size beyond what Low can achieve. You might need to support a custom link.xml file, and some reflection code paths might not behave the same. | |
| High | UnityLinker will strip as much code as possible. This will further reduce code size beyond what Medium can achieve but managed code debugging of some methods might no longer work. You might need to support a custom link.xml file, and some reflection code paths might not behave the same. | |
| Vertex Compression | Sets vertex compression per channel. This affects all the meshes in your project. Typically, Vertex Compression is used to reduce the size of mesh data in memory, reduce file size, and improve GPU performance. For more information on how to configure vertex compression and limitations of this setting, refer to Compressing mesh data. |
|
| Optimize Mesh Data | Enable this option to strip unused vertex attributes from the mesh used in a build. This option reduces the amount of data in the mesh, which can help reduce build size, loading times, and runtime memory usage. Warning: If you have this setting enabled, don’t change material or shader settings at runtime. For more information, refer to PlayerSettings.stripUnusedMeshComponents. |
|
| Texture Mipmap Stripping | Enables mipmap stripping for all platforms. It strips unused mipmap levels from Textures at build time. Unity determines unused mipmap levels by comparing the mipmap level against the quality settings for the current platform. If a mipmap level is excluded from every quality setting for the current platform, then Unity strips those mipmap levels from the build at build time. If QualitySettings.globalTextureMipmapLimit is set to a mipmap level that has been stripped, Unity will set the value to the closest mipmap level that hasn’t been stripped. |
|
Stack Trace
Select your preferred logging type by enabling the option that corresponds to each Log Type.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| None | No logs are ever recorded. |
| ScriptOnly | Logs only when running scriptsA piece of code that allows you to create your own Components, trigger game events, modify Component properties over time and respond to user input in any way you like. More info See in Glossary. |
| Full | Logs all the time. |
For more information, refer to stack trace logging.
Legacy

| Property | Function |
|---|---|
| Clamp BlendShapes (Deprecated) | Enable the option to clamp the range of blend shape weights in SkinnedMeshRenderers. |