About ARKit XR Plug-in
Use the ARKit XR Plug-in package to enable ARKit support via Unity's multi-platform XR API. This package implements the following XR Subsystems:
- Session
- Camera
- Depth
- Input
- Planes
- Raycast
- Anchors
- Image tracking
- Environment probes
- Body tracking
- Occlusion
- Participant
- Meshes
This version of ARKit XR Plug-in supports the following features:
- Device localization
- Horizontal plane detection
- Vertical plane detection
- Point clouds
- Pass-through camera view
- Light estimation
- Anchors
- Hit testing
- Session management
- Image tracking
- Object tracking
- Environment probes
- Participant tracking
- Meshes (also known as Scene Reconstruction)
- Occlusion
Important
Apple's App Store rejects any app that contains certain face tracking-related symbols in its binary if the app developer doesn't intend to use face tracking. To avoid ambiguity, face tracking support is available in a separate package, ARKit Face Tracking.
Installing ARKit XR Plug-in
To install this package, follow the instructions in the Package Manager documentation.
In addition, install the AR Foundation package, which uses ARKit XR Plug-in and provides many useful scripts and Prefabs. For more information about this package, see the AR Foundation documentation.
Using ARKit XR Plug-in
The ARKit XR Plug-in implements the native iOS endpoints required for building Handheld AR apps using Unity's multi-platform XR API. However, this package doesn't expose any public scripting interface of its own. In most cases, you should use the scripts, Prefabs, and assets provided by AR Foundation as the basis for your Handheld AR apps.
Including the ARKit XR Plug-in also includes source files, static libraries, shader files, and plug-in metadata.
ARKit requires iOS 11.0. Some specific features require later versions (see below).
Build settings
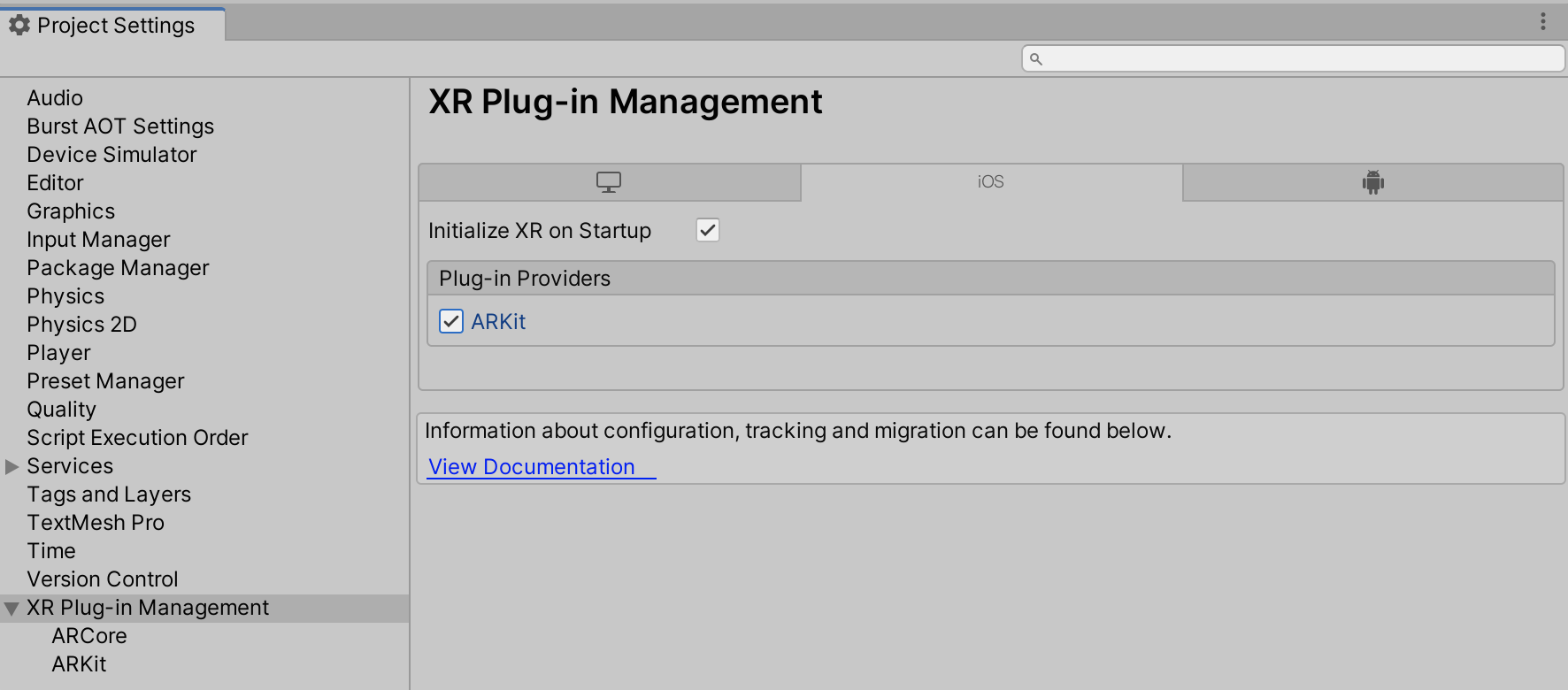
To access ARKit build settings, from Unity's main menu, go to Edit > Project Settings, then navigate to the XR Plug-in Management menu and enable the ARKit provider, as shown in the screenshot below:
This creates an ARKitSettings asset that you can access under XR Plug-in Management > ARKit, as shown in the screenshot below:
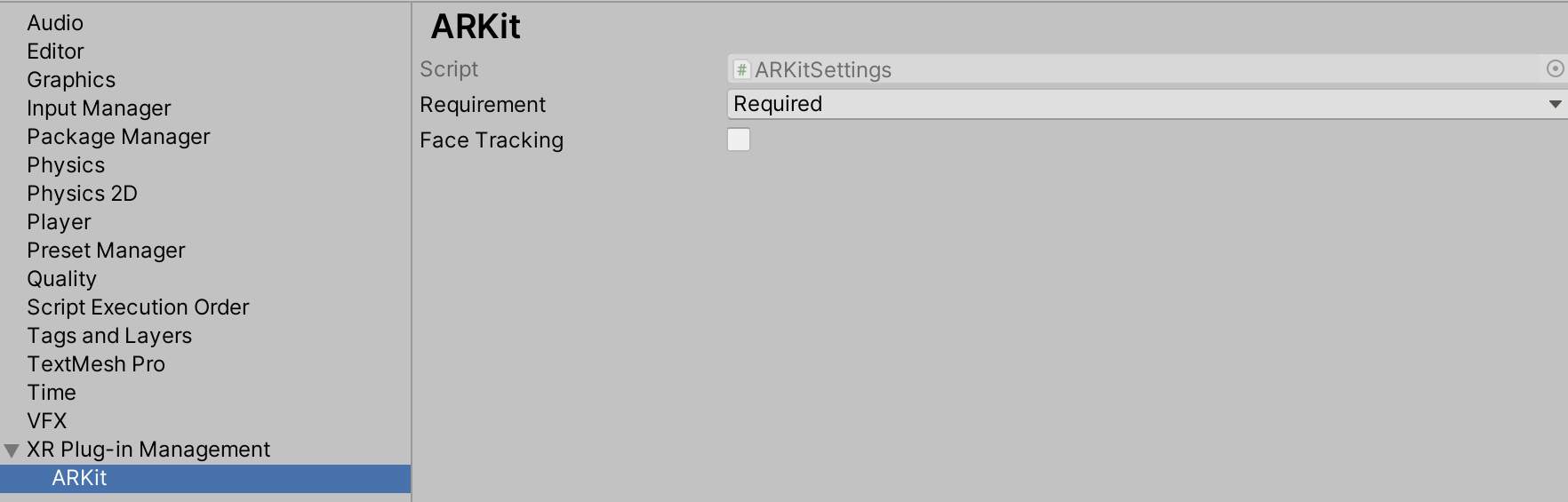
Requiring AR
You can flag ARKit as either required or optional. By default, ARKit is required, which means your app can only be installed on AR-supported devices and operating systems (iOS 11.0 and above). If you specify that AR is optional, your app can be installed on all iOS devices.
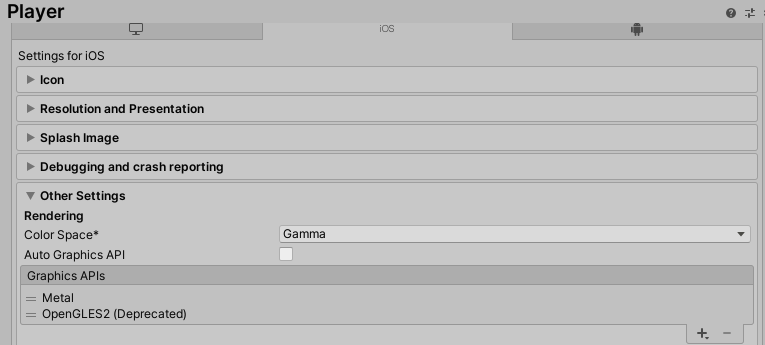
Targeting 32-bit devices
To target 32-bit devices, OpenGLES2 must be included in the list of Graphics APIs. From Unity's main menu, go to Edit > Project Settings, then navigate to Player > Other Settings > Graphics APIs, as shown in the screenshot below:
Session
ARKit implements XRSessionSubsystem.GetAvailabilityAsync, which consists of the device checking that it's running on iOS 11.0 or above. For more information, see the ARSubsystems session documentation.
Depth subsystem
Raycasts always return a Pose for the item the raycast hit. When raycasting against feature points, the pose is oriented to provide an estimate for the surface the feature point might represent.
The depth subsystem doesn't require additional resources, so enabling it doesn't affect performance
ARKit's depth subsystem only ever produces a single XRPointCloud.
For more information, see the ARSubsystems depth subsystem documentation.
Plane tracking
ARKit doesn't support plane subsumption (that is, one plane can't be included in another plane); there is no merge event. If two planes are determined to be separate parts of the same surface, one plane might be removed while the other expands to the explored surface.
ARKit provides boundary points for all its planes on iOS 11.3 and later.
The ARKit plane subsystem requires additional CPU resources and can be energy-intensive. Enabling both horizontal and vertical plane detection (available in iOS 11.3+) requires additional resources. Consider disabling plane detection when your app doesn't need it to save energy.
Setting the plane detection mode to PlaneDetectionMode.None is equivalent to calling Stop() on the subsystem.
For more information, see the ARSubsystems plane subsystem documentation.
Participant tracking
A participant represents another device in a multi-user collaborative session. Although you can start and stop the participant subsystem at any time, the session must receive ARCollaborationData from other peers in the multi-user session in order for participants to be detected. For an example implementation, see the ARCollaborationData sample on GitHub.
Light estimation
ARKit light estimation can only be enabled or disabled. The availability of either Ambient Intensity or Environmental HDR data is governed by the active tracking mode. See the following table for more details.
| Tracking configuration | Ambient intensity (lumens) | Color temperature | Main light direction | Main light intensity (lumens) | Ambient spherical harmonics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World Tracking | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Face Tracking | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Camera configuration
XRCameraConfiguration contains an IntPtr field nativeConfigurationHandle which is a platform-specific handle. For ARKit, this handle is a pointer to the native ARVideoFormat Objective-C object.
Technical details
Requirements
This version of ARKit XR Plug-in is compatible with the following versions of the Unity Editor:
- 2020.3
- 2021.1
- 2021.2
You must use Xcode 12 or later when compiling an iOS Player that includes this package.
Known limitations
- Color correction is not available as an RGB Value (only as color temperature).
Package contents
This version of ARKit XR Plug-in includes:
- A static library which provides implementation of the XR Subsystems listed above
- An Objective-C source file
- A shader used for rendering the camera image
- A plug-in metadata file