从深度纹理重建像素的世界空间位置
本示例中的 Unity Shader 使用深度纹理和屏幕空间 UV 坐标
重建像素的世界空间位置,并在网格上绘制棋盘格图案以可视化重建的坐标。
最终效果如下:
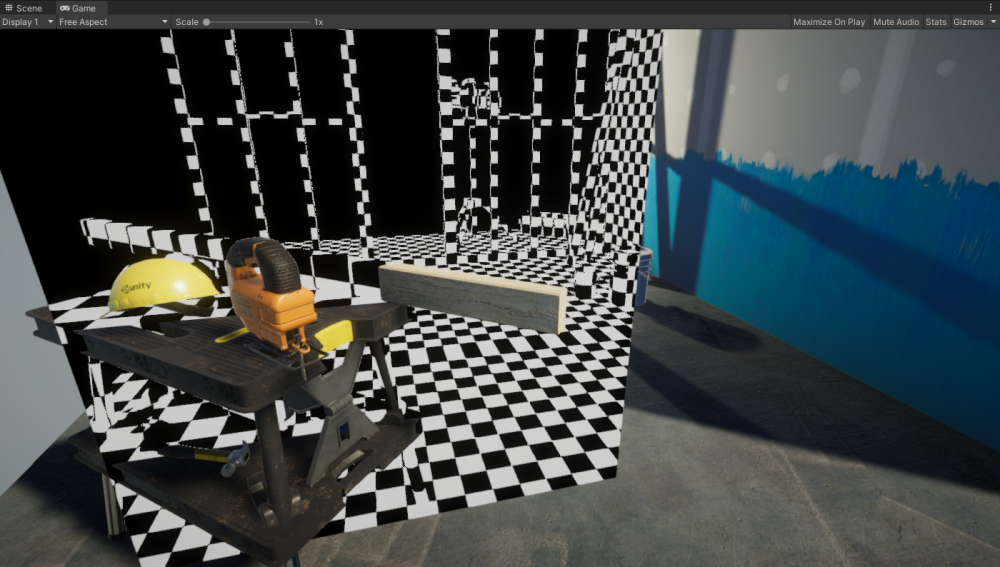
本页面包含以下部分:
创建示例场景
按以下步骤创建示例场景:
在现有 Unity 项目中安装 URP,或使用
通用渲染管线模板(Universal Project Template) 创建新项目。在示例场景中创建一个 Plane GameObject,
并放置在场景中使其遮挡部分物体。
创建一个新材质(Material),并分配给 Plane。
创建一个新 Shader 并分配给该材质。
复制并粘贴 URP Unlit 基础 Shader 的代码。选择 URP 资源(URP Asset)。
- 如果项目是使用 URP 模板创建的,URP 资源路径为:
Assets/Settings/UniversalRP-HighQuality
- 如果项目是使用 URP 模板创建的,URP 资源路径为:
在 URP 资源的 General 部分,启用
Depth Texture。
打开在步骤 4 创建的 Shader,准备进行修改。
编辑 ShaderLab 代码
本部分假设你已从 URP Unlit 基础 Shader 复制了源码。
对 ShaderLab 代码进行以下修改:
在
HLSLPROGRAM块中,添加 深度纹理 Shader 头文件 的#include语句,
可放置在Core.hlsl之后:#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/Core.hlsl" // DeclareDepthTexture.hlsl 提供了采样相机深度纹理的工具函数 #include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/DeclareDepthTexture.hlsl"DeclareDepthTexture.hlsl文件提供了用于采样相机深度纹理的函数,
本示例使用SampleSceneDepth函数获取像素的 Z 坐标。在 片元着色器(fragment shader)定义中,添加
Varyings IN作为输入参数:half4 frag(Varyings IN) : SV_Target本示例的片元着色器使用
Varyings结构体中的positionHCS变量来获取像素位置。在片元着色器中,计算用于采样深度缓冲区的 UV 坐标,
需要使用positionHCS位置除以_ScaledScreenParams(渲染目标分辨率):float2 UV = IN.positionHCS.xy / _ScaledScreenParams.xy;_ScaledScreenParams.xy考虑了渲染目标的缩放,如 动态分辨率(Dynamic Resolution)。使用
SampleSceneDepth采样深度缓冲区:#if UNITY_REVERSED_Z real depth = SampleSceneDepth(UV); #else // 调整 Z 值以匹配 OpenGL 的 NDC 空间 real depth = lerp(UNITY_NEAR_CLIP_VALUE, 1, SampleSceneDepth(UV)); #endifSampleSceneDepth由DeclareDepthTexture.hlsl提供,返回[0, 1]之间的 Z 值。注意:
ComputeWorldSpacePosition计算世界空间位置时,深度值必须在 NDC(归一化设备坐标)空间。- 在 D3D 中,Z 取值范围为
[0,1],
在 OpenGL 中,Z 取值范围为[-1, 1]。 UNITY_REVERSED_Z用于区分平台并调整 Z 值范围。UNITY_NEAR_CLIP_VALUE是平台无关的近平面裁剪值。
详细信息请参考 平台特定渲染差异。
重建像素的世界空间坐标:
float3 worldPos = ComputeWorldSpacePosition(UV, depth, UNITY_MATRIX_I_VP);ComputeWorldSpacePosition从 UV 和深度(Z)计算世界空间位置,
该函数定义于 SRP Core 包的Common.hlsl文件中。UNITY_MATRIX_I_VP是逆视图投影矩阵,用于将裁剪空间坐标转换为世界空间。
可视化世界空间位置(棋盘格效果):
uint scale = 10; uint3 worldIntPos = uint3(abs(worldPos.xyz * scale)); bool white = (worldIntPos.x & 1) ^ (worldIntPos.y & 1) ^ (worldIntPos.z & 1); half4 color = white ? half4(1,1,1,1) : half4(0,0,0,1);scale控制棋盘格的大小(值越大,格子越小)。abs(worldPos.xyz * scale)确保棋盘格在负坐标方向上对称。uint3将坐标转换为整数,以对齐棋盘格。& 1检查坐标是否为奇数或偶数:- 偶数返回 0,奇数返回 1。
- 这使得代码可以将表面划分为正方形区域。
^(XOR)翻转颜色,形成棋盘格效果。
处理深度缓冲区无效区域(无几何体渲染):
#if UNITY_REVERSED_Z if(depth < 0.0001) return half4(0,0,0,1); #else if(depth > 0.9999) return half4(0,0,0,1); #endif不同平台的远裁剪平面 Z 值不同:
- D3D:远平面 Z = 1(UNITY_REVERSED_Z 开启)
- OpenGL:远平面 Z = 0(UNITY_REVERSED_Z 关闭)
UNITY_REVERSED_Z变量确保不同平台正确处理深度值。保存 Shader 代码,示例已准备就绪。
最终效果:

完整的 ShaderLab 代码
以下是本示例的完整 ShaderLab 代码:
// This Unity shader reconstructs the world space positions for pixels using a depth
// texture and screen space UV coordinates. The shader draws a checkerboard pattern
// on a mesh to visualize the positions.
Shader "Example/URPReconstructWorldPos"
{
Properties
{ }
// The SubShader block containing the Shader code.
SubShader
{
// SubShader Tags define when and under which conditions a SubShader block or
// a pass is executed.
Tags { "RenderType" = "Opaque" "RenderPipeline" = "UniversalPipeline" }
Pass
{
HLSLPROGRAM
// This line defines the name of the vertex shader.
#pragma vertex vert
// This line defines the name of the fragment shader.
#pragma fragment frag
// The Core.hlsl file contains definitions of frequently used HLSL
// macros and functions, and also contains #include references to other
// HLSL files (for example, Common.hlsl, SpaceTransforms.hlsl, etc.).
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/Core.hlsl"
// The DeclareDepthTexture.hlsl file contains utilities for sampling the
// Camera depth texture.
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/DeclareDepthTexture.hlsl"
// This example uses the Attributes structure as an input structure in
// the vertex shader.
struct Attributes
{
// The positionOS variable contains the vertex positions in object
// space.
float4 positionOS : POSITION;
};
struct Varyings
{
// The positions in this struct must have the SV_POSITION semantic.
float4 positionHCS : SV_POSITION;
};
// The vertex shader definition with properties defined in the Varyings
// structure. The type of the vert function must match the type (struct)
// that it returns.
Varyings vert(Attributes IN)
{
// Declaring the output object (OUT) with the Varyings struct.
Varyings OUT;
// The TransformObjectToHClip function transforms vertex positions
// from object space to homogenous clip space.
OUT.positionHCS = TransformObjectToHClip(IN.positionOS.xyz);
// Returning the output.
return OUT;
}
// The fragment shader definition.
// The Varyings input structure contains interpolated values from the
// vertex shader. The fragment shader uses the `positionHCS` property
// from the `Varyings` struct to get locations of pixels.
half4 frag(Varyings IN) : SV_Target
{
// To calculate the UV coordinates for sampling the depth buffer,
// divide the pixel location by the render target resolution
// _ScaledScreenParams.
float2 UV = IN.positionHCS.xy / _ScaledScreenParams.xy;
// Sample the depth from the Camera depth texture.
#if UNITY_REVERSED_Z
real depth = SampleSceneDepth(UV);
#else
// Adjust Z to match NDC for OpenGL ([-1, 1])
real depth = lerp(UNITY_NEAR_CLIP_VALUE, 1, SampleSceneDepth(UV));
#endif
// Reconstruct the world space positions.
float3 worldPos = ComputeWorldSpacePosition(UV, depth, UNITY_MATRIX_I_VP);
// The following part creates the checkerboard effect.
// Scale is the inverse size of the squares.
uint scale = 10;
// Scale, mirror and snap the coordinates.
uint3 worldIntPos = uint3(abs(worldPos.xyz * scale));
// Divide the surface into squares. Calculate the color ID value.
bool white = ((worldIntPos.x) & 1) ^ (worldIntPos.y & 1) ^ (worldIntPos.z & 1);
// Color the square based on the ID value (black or white).
half4 color = white ? half4(1,1,1,1) : half4(0,0,0,1);
// Set the color to black in the proximity to the far clipping
// plane.
#if UNITY_REVERSED_Z
// Case for platforms with REVERSED_Z, such as D3D.
if(depth < 0.0001)
return half4(0,0,0,1);
#else
// Case for platforms without REVERSED_Z, such as OpenGL.
if(depth > 0.9999)
return half4(0,0,0,1);
#endif
return color;
}
ENDHLSL
}
}
}