了解视锥体
视锥体 一词表示看起来像顶部切割后平行于底部的金字塔的实体形状。这是透视摄像机可以看到和渲染的区域的形状。以下思维实验应该有助于解释为什么会这样。
想象一下,将一根直杆(例如扫帚柄或一支铅笔)正对着摄像机,然后拍照。如果杆垂直于摄像机镜头保持在图片中心位置,那么只有其一端可在图片上显示为圆圈;所有其他部分都会被遮挡。如果将杆向上移动,下侧将开始变得可见,但可通过向上倾斜杆再次将其隐藏。如果继续向上移动杆并进一步将其向上倾斜,则圆形末端最终将到达图片的顶部边缘。此时,在世界空间中由此杆跟踪的界线上方的任何对象在图片上都不可见。
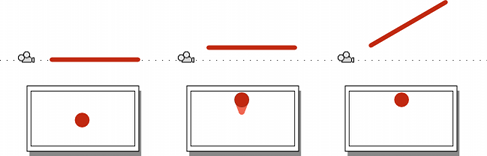
很容易将杆向左、向右或向下(或者水平和垂直方向的任何组合方式)移动或旋转。“隐藏”杆的角度仅取决于它在两个轴上距离屏幕中心的距离。
这一思维实验的意义在于,摄像机图像中的任何一点实际上都对应于世界空间中的一条线,在图像中只能看到这条线上的一个点。这条线上该位置背后的一切都会被遮挡。
图像的外边缘由对应于图像四个角的发散线界定。如果这些线向后追踪到摄像机,它们最终会聚合到同一个点。在 Unity 中,此点恰好位于摄像机的变换位置,也称为透视中心。从屏幕顶部和底部中心聚合到透视中心处的线所形成的角度称为视野(通常缩写为 FOV)。
如上所述,任何落在图像边缘的发散线之外的物体对摄像机而言均不可见,但是针对摄像机渲染的内容还有另外两个限制。近剪裁面和远剪裁面平行于摄像机的 XY 平面,两者沿中心线相隔一定的距离。比近剪裁面更靠近摄像机的任何对象以及比远裁剪面更远离摄像机的任何对象都不会被渲染。

图像的发散角线以及两个裁剪面定义了截头金字塔:视锥体。
The far clipping plane and floating point math
Objects, lights, and shadows might flicker if they’re far away. The flickering occurs because distances are too large to calculate positions precisely with floating point math. In each frame, the object, light, or shadow is at a slightly different position, so it moves in and out of the view frustum.
Minimise flickering using one of the following approaches:
- Reduce the far clipping plane distance in the Camera component to avoid the distance of objects becoming too large for precise calculations.
- Make everything in your scene smaller, to reduce distances across your whole scene.
Unity calculates lights and shadows with the world space position as the reference point, for example 0, 0, 0 in a 3D scene. Flickering occurs when lights and shadows are far away from the world space position. To minimise flickering, you can enable camera-relative culling, so Unity uses the camera position as the relative position for shadow calculations. See Culling settings in Graphics settings.