Description
Interface into the Gyroscope.
Use this class to access the gyroscope. The example script below shows how the Gyroscope class can be used to view the orientation in space of the iOS device.
#pragma strict // iOS gyroscope example // // Create a cube with camera vector names on the faces. // Allow the iPhone to show named faces as it is oriented. public class ExampleScript extends MonoBehaviour { private var quads: GameObject[] = new GameObject[6]; public var labels: Texture[]; function Start() { // make camera solid colour and based at the origin GetComponent.<Camera>().backgroundColor = new Color(49.0f / 255.0f, 77.0f / 255.0f, 121.0f / 255.0f); GetComponent.<Camera>().transform.position = new Vector3(0, 0, 0); GetComponent.<Camera>().clearFlags = CameraClearFlags.SolidColor; // create the six quads forming the sides of a cube var quad: GameObject = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Quad); quads[0] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3(1, 0, 0), new Vector3(0, 90, 0), "plus x", new Color(0.90f, 0.10f, 0.10f, 1), labels[0]); quads[1] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3(0, 1, 0), new Vector3(-90, 0, 0), "plus y", new Color(0.10f, 0.90f, 0.10f, 1), labels[1]); quads[2] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3(0, 0, 1), new Vector3(0, 0, 0), "plus z", new Color(0.10f, 0.10f, 0.90f, 1), labels[2]); quads[3] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3(-1, 0, 0), new Vector3(0, -90, 0), "neg x", new Color(0.90f, 0.50f, 0.50f, 1), labels[3]); quads[4] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3(0, -1, 0), new Vector3(90, 0, 0), "neg y", new Color(0.50f, 0.90f, 0.50f, 1), labels[4]); quads[5] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3(0, 0, -1), new Vector3(0, 180, 0), "neg z", new Color(0.50f, 0.50f, 0.90f, 1), labels[5]); GameObject.Destroy(quad); } // make a quad for one side of the cube function createQuad(quad: GameObject, pos: Vector3, rot: Vector3, name: String, col: Color, t: Texture) { var quat: Quaternion = Quaternion.Euler(rot); var GO: GameObject = Instantiate(quad, pos, quat); GO.name = name; GO.GetComponent.<Renderer>().material.color = col; GO.GetComponent.<Renderer>().material.mainTexture = t; GO.transform.localScale += new Vector3(0.25f, 0.25f, 0.25f); return GO; } protected function Update() { GyroModifyCamera(); } protected function OnGUI() { GUI.skin.label.fontSize = Screen.width / 40; GUILayout.Label("Orientation: " + Screen.orientation); GUILayout.Label("input.gyro.attitude: " + Input.gyro.attitude); GUILayout.Label("iphone width/font: " + Screen.width + " : " + GUI.skin.label.fontSize); } // Make the necessary change to the camera. function GyroModifyCamera() { transform.rotation = GyroToUnity(Input.gyro.attitude); } private static function GyroToUnity(q: Quaternion) { return new Quaternion(q.x, q.y, -q.z, -q.w); } }
// iOS gyroscope example // // Create a cube with camera vector names on the faces. // Allow the iPhone to show named faces as it is oriented.
using UnityEngine; using UnityEngine.iOS;
public class ExampleScript : MonoBehaviour {
// Faces for 6 sides of the cube private GameObject[] quads = new GameObject[6];
// Textures for each quad, should be +X, +Y etc // with appropriate colors, red, green, blue, etc public Texture[] labels;
void Start () { // make camera solid colour and based at the origin GetComponent<Camera>().backgroundColor = new Color(49.0f/255.0f, 77.0f/255.0f, 121.0f/255.0f); GetComponent<Camera>().transform.position = new Vector3(0, 0, 0); GetComponent<Camera>().clearFlags = CameraClearFlags.SolidColor;
// create the six quads forming the sides of a cube GameObject quad = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Quad);
quads[0] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3( 1, 0, 0), new Vector3( 0, 90, 0), "plus x", new Color(0.90f, 0.10f, 0.10f, 1), labels[0]); quads[1] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3( 0, 1, 0), new Vector3(-90, 0, 0), "plus y", new Color(0.10f, 0.90f, 0.10f, 1), labels[1]); quads[2] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3( 0, 0, 1), new Vector3( 0, 0, 0), "plus z", new Color(0.10f, 0.10f, 0.90f, 1), labels[2]); quads[3] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3(-1, 0, 0), new Vector3( 0, -90, 0), "neg x", new Color(0.90f, 0.50f, 0.50f, 1), labels[3]); quads[4] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3( 0, -1, 0), new Vector3( 90, 0, 0), "neg y", new Color(0.50f, 0.90f, 0.50f, 1), labels[4]); quads[5] = createQuad(quad, new Vector3( 0, 0, -1), new Vector3( 0, 180, 0), "neg z", new Color(0.50f, 0.50f, 0.90f, 1), labels[5]);
GameObject.Destroy(quad); }
// make a quad for one side of the cube GameObject createQuad(GameObject quad, Vector3 pos, Vector3 rot, string name, Color col, Texture t) { Quaternion quat = Quaternion.Euler(rot); GameObject GO = Instantiate(quad, pos, quat); GO.name = name; GO.GetComponent<Renderer>().material.color = col; GO.GetComponent<Renderer>().material.mainTexture = t; GO.transform.localScale += new Vector3(0.25f, 0.25f, 0.25f); return GO; }
protected void Update() { GyroModifyCamera(); }
protected void OnGUI() { GUI.skin.label.fontSize = Screen.width/40; GUILayout.Label("Orientation: " + Screen.orientation); GUILayout.Label("input.gyro.attitude: " + Input.gyro.attitude); GUILayout.Label("iphone width/font: " + Screen.width + " : " + GUI.skin.label.fontSize); }
/********************************************/
// The Gyroscope is right-handed. Unity is left handed. // Make the necessary change to the camera. void GyroModifyCamera() { transform.rotation = GyroToUnity(Input.gyro.attitude); }
private static Quaternion GyroToUnity(Quaternion q) { return new Quaternion(q.x, q.y, -q.z, -q.w); } }
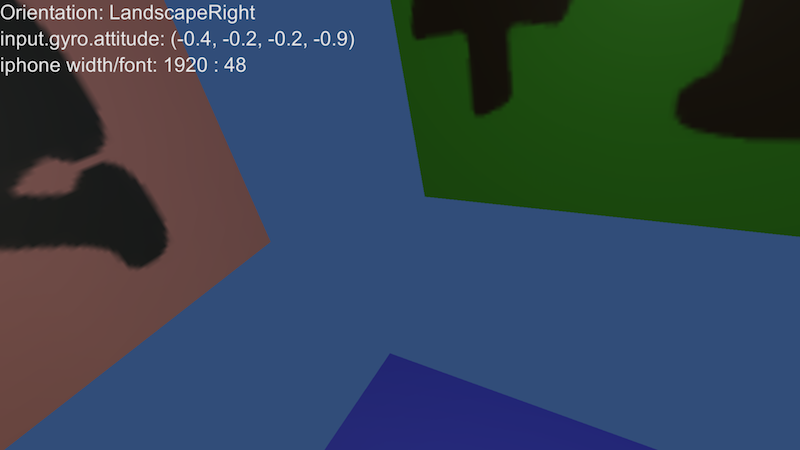
iOS Screen-shot showing +Z, +Y and -X
Variables
| attitude | Returns the attitude (ie, orientation in space) of the device. |
| enabled | Sets or retrieves the enabled status of this gyroscope. |
| gravity | Returns the gravity acceleration vector expressed in the device's reference frame. |
| rotationRate | Returns rotation rate as measured by the device's gyroscope. |
| rotationRateUnbiased | Returns unbiased rotation rate as measured by the device's gyroscope. |
| updateInterval | Sets or retrieves gyroscope interval in seconds. |
| userAcceleration | Returns the acceleration that the user is giving to the device. |
Copyright © 2023 Unity Technologies
优美缔软件(上海)有限公司 版权所有
"Unity"、Unity 徽标及其他 Unity 商标是 Unity Technologies 或其附属机构在美国及其他地区的商标或注册商标。其他名称或品牌是其各自所有者的商标。
公安部备案号:
31010902002961