Android のシンボル
アプリケーションのデバッグを支援するために、Unity のネイティブライブラリのシンボルファイルを含むパッケージを生成することができます。シンボルファイルには、アクティブなメモリアドレスをメソッド名などの使用可能な情報に変換するテーブルが含まれています。この変換プロセスをシンボル化と呼びます。シンボルパッケージを Google Play Console にアップロードすると、Android Vitals ダッシュボードで人間が読めるスタックトレースを表示できます。
シンボルファイルには 2 種類あります。
- Public: A small file that contains a symbol table. For more information, refer to Public symbols.
- Debug: Contains everything that a public symbol file contains, and full debugging information that you can use for more in-depth debugging. For more information, refer to Debugging symbols.
以下のライブラリのシンボルファイルを生成することができます。
-
libmain: 最初の Unity エンジンのロードロジック関連。 -
libunity: Unity のエンジンコード。 -
libil2cpp: C++ コードに変換したプロジェクトからの C# スクリプトを含みます。
Unity は、libmain と libunity のシンボルファイルを生成します。Gradle は、libil2cpp のシンボルファイルを生成します。
パブリックシンボル
パブリックシンボルファイルには、関数のアドレスを人間が読める文字列に解決する情報が含まれています。Unity は --strip-debug パラメーターを使用して、詳細なデバッグ情報を削除したパブリックシンボルを作成します。これにより、パブリックシンボルファイルとパッケージは、デバッグシンボル ファイルとパッケージよりも小さくなります。
デバッグシンボル
デバッグシンボルファイルには、完全なデバッグ情報とシンボルテーブルが含まれています。それを使って以下を行えます。
- スタックトレースを解決し、ソースコードが利用可能なアプリケーションをデバッグすることができます。
- アプリケーションにネイティブデバッガーを取り付け、コードをデバッグします。
Unity uses the --only-keep-debug parameter to create debugging symbols. For more information, refer to –only-keep-debug in the Linux user manual.
Note: If debugging symbols aren’t available, Unity places a public symbol file in your project at build time. For the libmain and libunity libraries, debugging symbols aren’t available and Unity always generates public symbol files.
Custom symbols
You can instruct Unity to include additional symbol files. This is useful if you use shared libraries and want your local debugger, and Google Play, to resolve the shared library stack traces if the application crashes.
To make Unity include a custom symbols file:
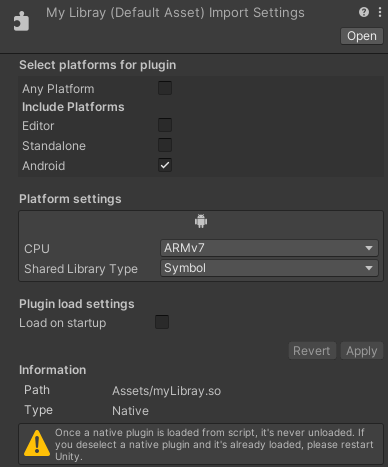
- In the Project window, select a plug-in that has a
.sofile extension. - In the Inspector, find the Platform settings section.
- Set CPU to the CPU architecture that the symbols file is compatible with.
- Set Shared Library Type to Symbol.
Whenever Unity generates a symbols package, it adds the additional symbol files to the symbols package.
If you want to make Unity include a custom symbols file from a C# script, the UnityEditor.Android namespace includes the following APIs to set the CPU and Shared Library Type respectively:
Note: The symbols file name must match the name of the shared library that the symbols file is for. For example, if a shared library is called mylibrary.so, the symbols file must also be named mylibrary.so. To avoid file name collisions, the symbols file and the shared library must be in separate directories.
Important: Ensure the symbols file is up to date and compatible with the shared library that contains the executable code. If you don’t, your local debugger and Google Play will fail to resolve stack traces for code in the shared library.
シンボルパッケージの生成
There are two ways to enable symbols package generation for your application:
- Through the Build Settings window.
- Using the EditorUserBuildSettings.androidCreateSymbols API.
To enable symbols package generation through the Build Settings window:
Build Settings ウィンドウを開きます (File > Build Settings)。
Select the Android platform.
-
Set Create symbols.zip to one of the following:
After you enable symbols package generation, building your project generates a .zip file that contains symbol files for the libmain and libunity library. If you set your scripting backend to IL2CPP, the .zip also contains a symbol file for the libil2cpp library. Unity places this symbols package within the output directory.
If you enable Export Project in the Android Build Settings, Unity doesn’t build the project. Instead, it exports the project for Android Studio, generates symbols for libmain and libunity, and places them within unityLibrary/symbols/<architecture>/ in the output directory. When you build your exported project from Android Studio, Gradle generates the libil2cpp symbol file and places it within the unityLibrary/symbols/<architecture>/ directory alongside the libmain and libunity symbol file.
Google Play コンソールでのシンボルの使用
After you upload your application to Google Play, you can upload a public symbols package for it. For information on how to do this, refer to Google’s documentation: Deobfuscate or symbolicate crash stack traces.
ノート: Google Play では、シンボルパッケージをアップロードする前にアプリケーションが受けたクラッシュはシンボル化されません。