- Unity User Manual 2022.3 (LTS)
- 사용자 인터페이스(UI) 생성
- UI 툴킷
- Style UI
- USS 선택자
- Class selectors
Class selectors
USS class selectors match elements that have specific USS classes assigned. USS class selectors are analogous to CSS class selectors.
구문
A class selector consists of the class name prefixed with a period. Class names are case-sensitive and can’t begin with a numeral.
.className { ... }
Only use a period when you write the selector in a USS file. Don’t include it when you assign the class to an element in a UXML or C# file. For example, don’t use <Button class=".yellow" />.
In general, don’t include a period in class names. Unity’s USS parser interprets a period as the beginning of a new class. For example, if you create a class called yellow.button, and create the following USS rule: .yellow.button{...}. The parser interprets the selector as a multiple selector, and tries to find elements that match both a .yellow class and a .button class.
요소에 두 개 이상의 클래스가 할당된 경우 선택자는 요소와 매칭되기 위해 이 중 하나와만 매칭되어야 합니다.
You can also specify multiple classes in a selector, in which case an element must have all of those classes assigned in order to match. See Multiple selectors for details.
예제
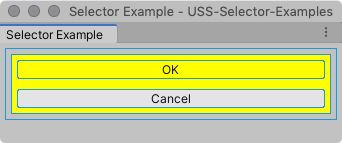
To demonstrate how simple selectors match elements, here is an example UI Document.
<UXML xmlns="UnityEngine.UIElements">
<VisualElement name="container1">
<VisualElement name="container2" class="yellow">
<Button name="OK" class="yellow" text="OK" />
<Button name="Cancel" text="Cancel" />
</VisualElement>
</VisualElement>
</UXML>
With no styles applied, the UI looks like the following:
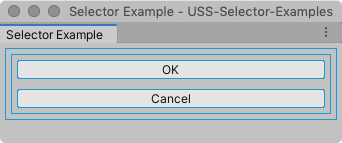
The following name class selector style rule matches the element container2 and the button element OK, and changes their background to yellow.
.yellow {
background-color: yellow;
}
The UI looks like the following when you apply the style: