Ambient Occlusion
The effect descriptions on this page refer to the default effects found within the post-processing stack.
The Ambient Occlusion post-processing effect approximates Ambient Occlusion in real time as a full-screen post-processing effect. It darkens creases, holes, intersections and surfaces that are close to each other. In real life, such areas tend to block out or occlude ambient light, hence they appear darker.
Note that the Ambient Occlusion effect is quite expensive in terms of processing time and generally should only be used on desktop or console hardware. Its cost depends purely on screen resolution and the effects parameters and does not depend on sceneA Scene contains the environments and menus of your game. Think of each unique Scene file as a unique level. In each Scene, you place your environments, obstacles, and decorations, essentially designing and building your game in pieces. More info
See in Glossary complexity as true Ambient Occlusion would.
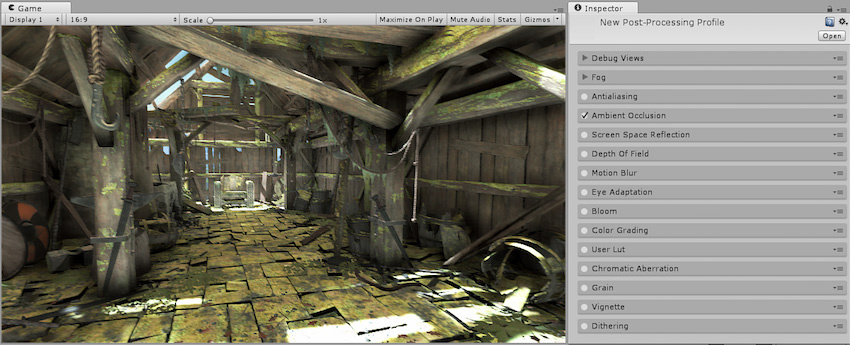
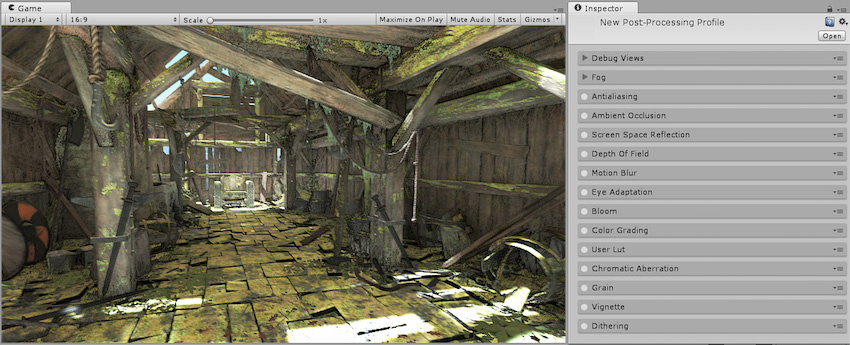
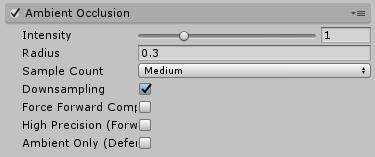
Properties
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Intensity | Degree of darkness produced by the effect. |
| Radius | Radius of sample points, which affects extent of darkened areas. |
| Sample Count | Number of sample points, which affects quality and performance. |
| Downsampling | Halves the resolution of the effect to increase performance at the cost of visual quality. |
| Force Forward Compatibility | Forces compatibility with Forward rendered objects when working with the Deferred rendering pathThe technique Unity uses to render graphics. Choosing a different path affects the performance of your game, and how lighting and shading are calculated. Some paths are more suited to different platforms and hardware than others. More info See in Glossary. |
| High Precision (Forward) | Toggles the use of a higher precision depth texture with the forward renderingA rendering path that renders each object in one or more passes, depending on lights that affect the object. Lights themselves are also treated differently by Forward Rendering, depending on their settings and intensity. More info See in Glossary path (may impact performances). Has no effect with the deferred renderingThe process of drawing graphics to the screen (or to a render texture). By default, the main camera in Unity renders its view to the screen. More info See in Glossary path. |
| Ambient Only | Enables the ambient-only mode in that the effect only affects ambient lighting. This mode is only available with the Deferred rendering path and HDRhigh dymanic range See in Glossary rendering. |
Optimisation
Reduce Radius size
Reduce Sample Count
Enable Downsampling
If using deferred rendering, disable Force Forward Compatibility (will cause forward rendered object to not be used when calculating Ambient Occlusion
If using forward rendering, disable High Precision (will cause the effect to use a lower precision depth texture, impacting visual quality)
Details
Beware that this effect can be quite expensive, especially when viewed very close to the cameraA component which creates an image of a particular viewpoint in your scene. The output is either drawn to the screen or captured as a texture. More info
See in Glossary. For that reason it is recommended to always enable Downsampling and favor a low radius setting. With a low radius the Ambient Occlusion effect will only sample pixelsThe smallest unit in a computer image. Pixel size depends on your screen resolution. Pixel lighting is calculated at every screen pixel. More info
See in Glossary that are close, in clip space, to the source pixel, which is good for performance as they can be cached efficiently. With higher radiuses, the generated samples will be further away from the source pixel and won’t benefit from caching thus slowing down the effect. Because of the camera__’s perspective, objects near the front plane will use larger radiuses than those far away, so computing the Ambient Occlusion pass for an object close to the camera__ will be slower than for an object further away that only occupies a few pixels on screen.
When working with the Deferred rendering path, you have the possibility to render the ambient occlusion straight to the ambient G-Buffer so that it’s taken into account by Unity during the lighting pass. Note that this setting requires the camera to have HDR enabled.
When working with the Forward rendering path you may experience some quality issues in regards to depth precision. You can overcome these issues by toggling High Precision but only do it if you actually need it as it will lower performances.
Requirements
Depth & Normals texture
ShaderA small script that contains the mathematical calculations and algorithms for calculating the Color of each pixel rendered, based on the lighting input and the Material configuration. More info
See in Glossary model 3
See the Graphics Hardware Capabilities and Emulation page for further details and a list of compliant hardware.
2017–05–24 Page published with no editorial review
New feature in 5.6