Vignette
The effect descriptions on this page refer to the default effects found within the post-processing stack.
In Photography, vignetting is the term used for the darkening and/or desaturating towards the edges of an image compared to the center. This is usually caused by thick or stacked filters, secondary lenses, and improper lens hoods. It is also often used for artistic effect, such as to draw focus to the center of an image.
The Vignette effect in the post-processing stack comes in 2 modes
Classic
Masked
Classic
Classic mode offers parametric controls for the position, shape and intensity of the Vignette. This is the most common way to use the effect.
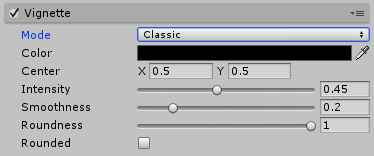
Properties
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Color | Vignette color. Use the alpha channel for transparency. |
| Center | Sets the vignette center point (screen center is [0.5,0.5]). |
| Intensity | Amount of vignetting on screen. |
| Smoothness | Smoothness of the vignette borders. |
| Roundness | Lower values will make a more squared vignette. |
| Rounded | Should the vignette be perfectly round or be dependent on the current aspect ratioThe relationship of an image’s proportional dimensions, such as its width and height. See in Glossary? |
Optimisation
- N/A
Requirements
- ShaderA small script that contains the mathematical calculations and algorithms for calculating the Color of each pixel rendered, based on the lighting input and the Material configuration. More info
See in Glossary model 3
See the Graphics Hardware Capabilities and Emulation page for further details and a list of compliant hardware.
Masked
Masked mode multiplies a custom texture mask over the screen to create a Vignette effect. This mode can be used to achieve less common vignetting effects.
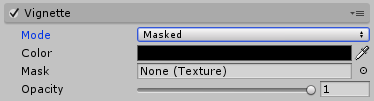
Properties
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Color | Vignette color. Use the alpha channel for transparency. |
| MaskCan refer to a Sprite Mask, a UI Mask, or a Layer Mask More info See in Glossary |
A black and white mask to use as a vignette. |
| Intensity | Mask opacity. |
Optimisation
- N/A
Requirements
- Shader model 3
See the Graphics Hardware Capabilities and Emulation page for further details and a list of compliant hardware.
2017–05–24 Page published with no editorial review
New feature in 5.6