Custom Render Textures
Switch to ScriptingCustom Render TexturesA special type of Texture that is created and updated at runtime. To use them, first create a new Render Texture and designate one of your Cameras to render into it. Then you can use the Render Texture in a Material just like a regular Texture. More info
See in Glossary are an extension to Render Textures that allows users to easily update said texture with a shader. This is useful to implement all kind of complex simulations like caustics, ripple simulation for rain effects, splatting liquids against a wall, etc. It also provides a scripting and ShaderA small script that contains the mathematical calculations and algorithms for calculating the Color of each pixel rendered, based on the lighting input and the Material configuration. More info
See in Glossary framework to help with more complicated configuration like partial or multi-pass updates, varying update frequency etc.
To use them, you need to create a new Custom Render Texture assetAny media or data that can be used in your game or Project. An asset may come from a file created outside of Unity, such as a 3D model, an audio file or an image. You can also create some asset types in Unity, such as an Animator Controller, an Audio Mixer or a Render Texture. More info
See in Glossary and assign a Material to it. This Material will then update the content of the texture according to its various parameters. The Custom Render Texture can then be assigned to any kind of Material just like a regular texture, even one used for another Custom Render Texture.
Properties
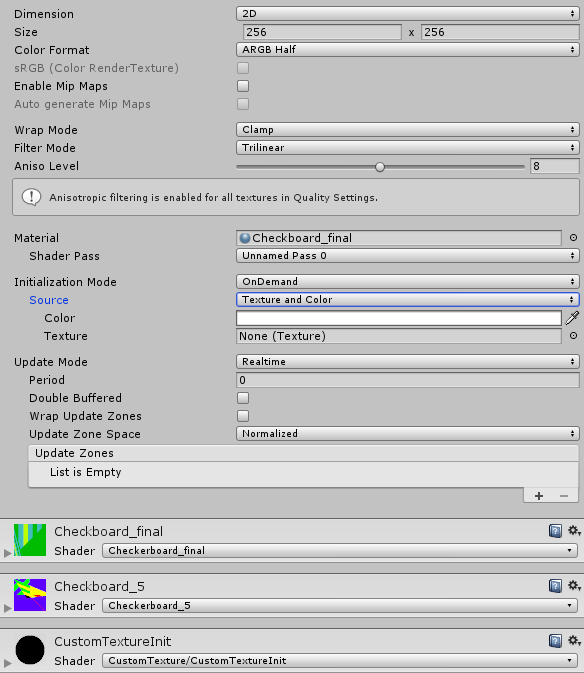
The inspectorA Unity window that displays information about the currently selected GameObject, Asset or Project Settings, alowing you to inspect and edit the values. More info
See in Glossary for Custom Render Textures will display most of the properties of the Render Texture inspector as well as many specific ones.
Render Texture:
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Dimension | Dimension of the Render Texture |
| 2D | Render Texture will be two dimensional. |
| Cube | Render Texture will be a cube map |
| 3D | Render Texture will be three dimensional |
| Size | The size of the Render Texture in pixelsThe smallest unit in a computer image. Pixel size depends on your screen resolution. Pixel lighting is calculated at every screen pixel. More info See in Glossary. |
| Color Format | Format of the Render Texture |
| sRGB (Color Render Texture) | Does this render texture use sRGB read/write conversions (Read Only). |
| Enable Mip Maps | Does this render texture use Mip Maps? |
| Auto generate Mip Maps | Enable to automatically generate Mip Maps. |
| Wrap Mode | Selects how the Texture behaves when tiled |
| Repeat | The Texture repeats (tiles) itself |
| Clamp | The Texture’s edges get stretched |
| Filter Mode | Selects how the Texture is filtered when it gets stretched by 3D transformations: |
| Point | The Texture becomes blocky up close |
| Bilinear | The Texture becomes blurry up close |
| Trilinear | Like Bilinear, but the Texture also blurs between the different mip levels |
| Aniso LevelThe anisotropic filtering (AF) level of a texture. Allows you to increase texture quality when viewing a texture at a steep angle. Good for floor and ground textures. More info See in Glossary |
Increases Texture quality when viewing the texture at a steep angle. Good for floor and ground textures |
Custom Texture:
Custom Texture parameters are separated in three main categories:
Material: Defines what shader is used to update the texture.
Initialization: Controls how the texture is initialized before any update is done by the shader
Update: Controls how the texture is updated by the shader.
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| MaterialAn asset that defines how a surface should be rendered, by including references to the Textures it uses, tiling information, Color tints and more. The available options for a Material depend on which Shader the Material is using. More info See in Glossary |
Material used to update the Custom Render Texture |
| Shader Pass | Shader Pass used to update the Custom Texture. The combo box will show all passes available in your Material. |
| Initialization Mode | Rate at which the texture should be initialized. |
| OnLoad | The texture is initialized once upon creation. |
| Realtime | The texture is initialized every frame. |
| OnDemand | The texture is initialized on demand from the script. |
| Source | How the texture should be initialized. |
| Texture and Color | The texture will be initialized by a texture multiplied by a color. |
| Initialization Color | Color with which the custom texture is initialized. If an initialization texture is provided as well, the custom texture will be initialized by the multiplication of the color and the texture. |
| Initialization Texture | Texture with which the custom texture is initialized. If an initialization color is provided as well, the custom texture will be initialized by the multiplication of the color and the texture. |
| Material | The texture will be initialized by a material. |
| Initialization Material | Material with which the custom texture is initialized. |
| Update Mode | Rate at which the texture should be updated by the shader. |
| OnLoad | The texture is updated once upon creation. |
| Realtime | The texture is updated every frame. |
| OnDemand | The texture is updated on demand from script. |
| Period | (Realtime only) Period in seconds at which real-time texture is updated (0.0 will update every frame). |
| Double Buffered | The texture will be double buffered. Each update will swap the two buffers, allowing user to read the result of the preceding update in the shader. |
| Wrap Update Zones | Enable to allow partial update zones to wrap around the border of the texture. |
| Cubemap Faces | (Cubemap only) Series of toggle allowing user to enable/disable update on each of the cubemapA collection of six square textures that can represent the reflections in an environment or the skybox drawn behind your geometry. The six squares form the faces of an imaginary cube that surrounds an object; each face represents the view along the directions of the world axes (up, down, left, right, forward and back). More info See in Glossary faces. |
| Update Zone Space | Coordinate system in which update zones are defined. |
| Normalized | All coordinates and sizes are between 0 and 1 with the top-left corner starting at (0, 0) |
| Pixel | All coordinates and sizes are expressed in pixels limited by the width and height of the texture. Top-left corner starting at (0, 0) |
| Update Zone List | List of update zones for the texture (see below for more details) |
Exporting Custom Render Texture to a file:
Custom Render Textures can be exported to a PNG or EXR file (depending on the texture format) via the contextual “Export” menu.
Update Zones:
By default, when the Custom Render Texture is updated, the whole texture is updated at once by the Material. One of the important features of the Custom Texture is the ability for the user to define zones of partial update. With this, users can define as many zones as they want and the order in which they are processed.
This can be used for several different purpose. For example, you could have multiple small zones to splat water drops on the texture and then do a full pass to simulate the ripples. This can also be used as an optimization when you know that you don’t need to update the full texture.

Update zones have their own set of properties. The Update Zone Space will be reflected in the display. Depending on the Dimension of the texture, coordinates will be 2D (for 2D and Cube textures) or 3D (for 3D textures).
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Center | Coordinate of the center of the update zone. |
| Size | Size of the update zone. |
| Rotation | Orientation of the update zone in degrees (unavailable for 3D textures). |
| Shader Pass | Shader Pass to use for this update zone. If left as default, this update zone will use the Shader Pass defined in the main part of the inspector otherwise it will use the provided one. |
| Swap (Double Buffer) | (Only for Double Buffered textures) If this is true, the buffers will be swapped before this update zone is processed. |
Double Buffered Custom Textures
Custom Render Textures can be “Double Buffered”. Internally, there are two textures but from the user standpoint they are the same. After each update, the two textures will be swapped. This allows the user to read the result of the last update while writing a new result in the Custom Render Texture. This is particularly useful if the shader needs to use the content already written in the texture but cannot mix the values with classic blend modes. This is also needed if the shaders has to sample different pixels of the preceding result.
Performance Warning: Due to some technicalities, the double buffering currently involves a copy of the texture at each swap which can lead to a drop in performance depending on the frequency at which it is done and the resolution of the texture.
Chaining Custom Render Textures
Custom Render Textures need a Material to be updated. This Material can have textures as input. This means that the a Custom Texture can be used as an input to generate another one. This way, users can chain up several Custom Textures to generate a more complex multi-step simulation. The system will correctly handle all the dependencies so that the different updates happen in the right order.
Writing a shader for a Custom Render Texture
Updating a Custom Texture is like doing a 2D post process in a Render Texture. To help users write their custom texture shaders, we provide a small framework with utility functions and built-in helper variables.
Here is a really simple example that will fill the texture with a color multiplied by a color:
Shader "CustomRenderTexture/Simple"
{
Properties
{
_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_Tex("InputTex", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader
{
Lighting Off
Blend One Zero
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#include "UnityCustomRenderTexture.cginc"
#pragma vertex CustomRenderTextureVertexShader
#pragma fragment frag
#pragma target 3.0
float4 _Color;
sampler2D _Tex;
float4 frag(v2f_customrendertexture IN) : COLOR
{
return _Color * tex2D(_Tex, IN.localTexcoord.xy);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
The only mandatory steps when writing a shader for a custom texture are:
* #include “UnityCustomRenderTexture.cginc”
Use the provided Vertex ShaderA program that runs on each vertex of a 3D model when the model is being rendered. More info
See in Glossary CustomRenderTextureVertexShaderUse the provided input structure v2f_customrendertexture for the pixel shader
Other than that, the user is free to write the pixel shader as he wishes.
Here is another example for a shader used in an initialization material:
Shader "CustomRenderTexture/CustomTextureInit"
{
Properties
{
_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_Tex("InputTex", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader
{
Lighting Off
Blend One Zero
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#include "UnityCustomRenderTexture.cginc"
#pragma vertex InitCustomRenderTextureVertexShader
#pragma fragment frag
#pragma target 3.0
float4 _Color;
sampler2D _Tex;
float4 frag(v2f_init_customrendertexture IN) : COLOR
{
_Color * tex2D(_Tex, IN.texcoord.xy);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
Same as for the update shader, the only mandatory steps are these:
* #include “UnityCustomRenderTexture.cginc”
Use the provided Vertex Shader InitCustomRenderTextureVertexShader
Use the provided input structure v2f_init_customrendertexture for the pixel shader
In order to help the user in this process we provide a set of built-in values:
Input values from the v2f_customrendertexture structure:
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
localTexcoord |
float3 |
Texture coordinates relative to the update zone being currently processed. |
globalTexcoord |
float3 |
Texture coordinates relative to the Custom Render Texture itself |
primitiveID |
uint |
Index of the update zone being currently processed. |
direction |
float3 |
For Cube Custom Render Texture, direction of the current pixel inside the cubemap. |
Input values from the v2f_init_customrendertexture structure:
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
texcoord |
float3 | Texture coordinates relative to the Custom Render Texture itself. |
Global values:
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
_CustomRenderTextureWidth |
float |
Width of the Custom Texture in pixels |
_CustomRenderTextureHeight |
float |
Height of the Custom Texture in pixels |
_CustomRenderTextureDepth |
float |
Depth of the Custom Texture in pixels (only for 3D textures, otherwise will always be equal to 1). |
_CustomRenderTextureCubeFace |
float |
Only for Cubemaps: Index of the current cubemap face being processed (-X, +X, -Y, +Y, -Z, +Z). |
_CustomRenderTexture3DSlice |
float |
Only for 3D textures: Index of the current 3D slice being processed. |
_SelfTexture2D |
Sampler2D |
For double buffered textures: Texture containing the result of the last update before the last swap. |
_SelfTextureCube |
SamplerCUBE |
For double buffered textures: Texture containing the result of the last update before the last swap. |
_SelfTexture3D |
Sampler3D |
For double buffered textures: Texture containing the result of the last update before the last swap. |
Controlling Custom Render Texture from Script
Most of the functionalities described here can be accessed via the Scripting API. Changing material parameters, update frequency, update zones, requesting an update etc, can all be done with the script.
One thing to keep in mind though is that any update requested for the Custom Texture will happen at a very specific time at the beginning of the frame with the current state of the Custom Texture. This guarantees that any material using this texture will have the up-to-date result.
This means that this kind of pattern:
customRenderTexture.updateZones = updateZones1;
customRenderTexture.Update();
customRenderTexture.updateZones = updateZones2;
customRenderTexture.Update();
Will not yield the “expected” result of one update done with the first array of update zones and then a second update with the other array. This will do two updates with the second array.
The good rule of thumb is that any property modified will only be active in the next frame.
2017–05–18 Page published with no editorial review
New feature in Unity 2017.1 NewIn20171